Zhang Zhen, Professor of Suzhou Institute of Advanced Research (SIAR), delivered a research paper entitled "Efficient Solar-osmotic Power Generation from Bioinspired Anti-fouling 2D WS2 Composite Membranes" at Angewandte Chemie International Edition.
Osmotic power, salinity gradient power or blue energy is the energy available from the difference in the salt concentration between seawater and river water. It is an ideal renewable energy with large reserves and stable daily changes, which could be directly converted into electricity by reverse electrodialysis technology so as to alleviate the energy crisis and environmental pollution. Osmotic energy is expected to be efficiently extracted by applying nanofluidic channel membranes with finite domain ion-transfer kinetics in reverse electrodialysis. Furthermore, 2D materials are regarded as ideal units for the construction of nanoflow channel membranes because of their natural interlayer channels, rich surface properties and great machinability, but it is necessary to modify the reconstructed 2D material film through a complex and costly process to improve its permeability and energy conversion.
In this study, a typical 2D material, tungsten disulfide, was used to construct a biomimetic composite membrane for solar-assisted high-performance osmotic energy conversion. Surface conditions of the nanoflow channel membrane such as temperature and charge density were synchronously regulated and controlled by applying illumination to establish a transmembrane temperature gradient and a transmembrane charge gradient, jointly promoting the transmembrane transport of cations. Together with theoretical simulation, it further revealed the synergy mechanism of external fields in regulating ion transport in nanoflow channels. The research drove the strategy of sustainable energy (solar energy and osmotic energy) coupling energy production, and disclosed external fields’ synergistic regulation mechanism of ion transport, thereby providing a universal strategy for addressing nanofluid energy conversion and other applications with similar concepts (such as ion screening and desalination).
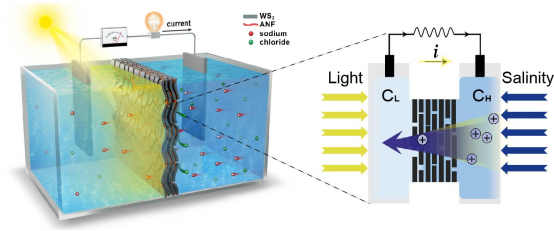
Schematic diagram of external field synergistically promoting osmotic energy conversion
The paper was completed by Prof. Zhang Zhen's SIAR team and Associate Prof. Wen Liping's team of CAS Institute of Physical and Chemical Technology. Prof. Zhang Zhen and Associate Prof. Wen Liping are the co-corresponding authors, while SIAR is the co-corresponding unit.
Paper link: https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202302938
SIAR Prof. Zhang Zhen Makes New Progress In Osmotic Energy Conversion
Publish Date:2023-05-11
Views:1092